| Magnetoelectric transducers |
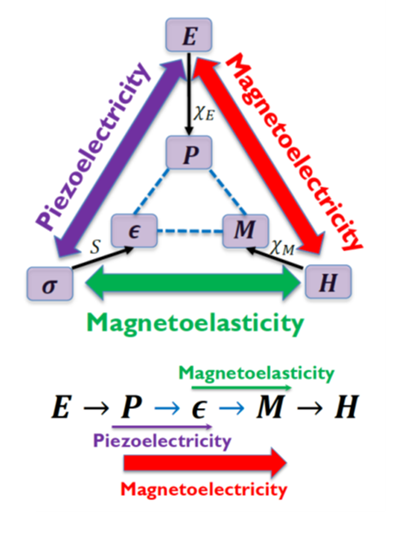
| To build logic circuits based on spin-wave majority gates that are competitive with CMOS-based technology, it is necessary to develop energy efficient transducers between spin-wave and electric domains so to cointegrate the two technologies in a single system. Key requirements of such transducers are high coupling efficiency, low operational power, and high bandwidth. Magnetoelectric transducers represent a scalable and low-power alternative consisting of a piezoelectric-magnetostrictive (PE-MS) bilayer in which the coupling between the electric and the spin domain occurs via strain. (details: Tierno et al. Microelectronic Engineering 187–188 (2018)). |
 |
|
|
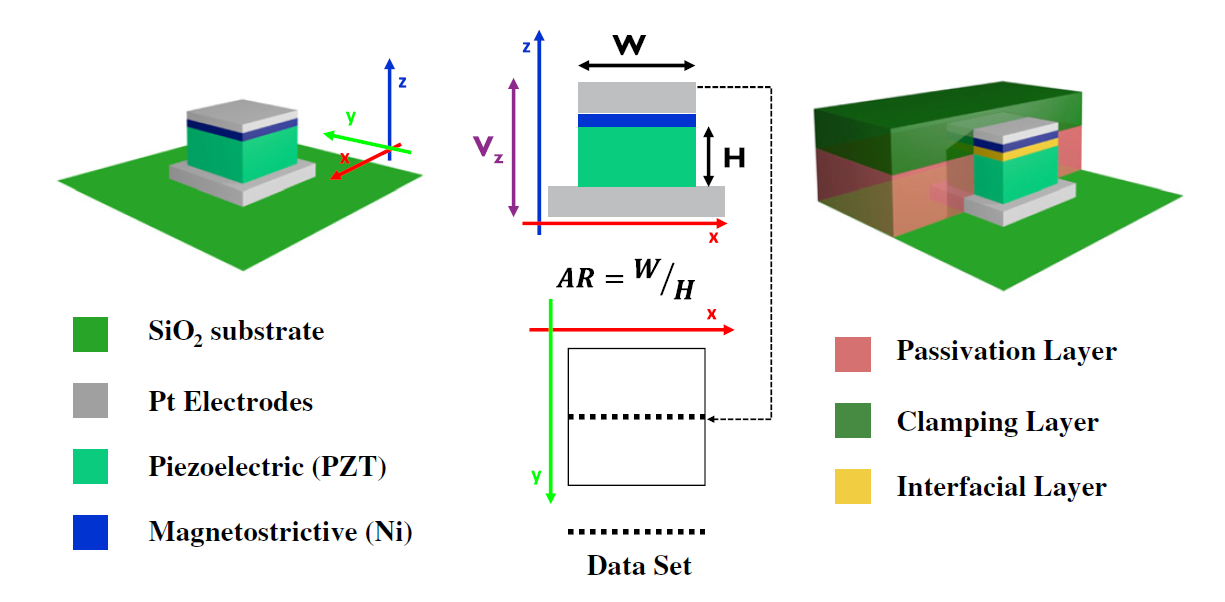
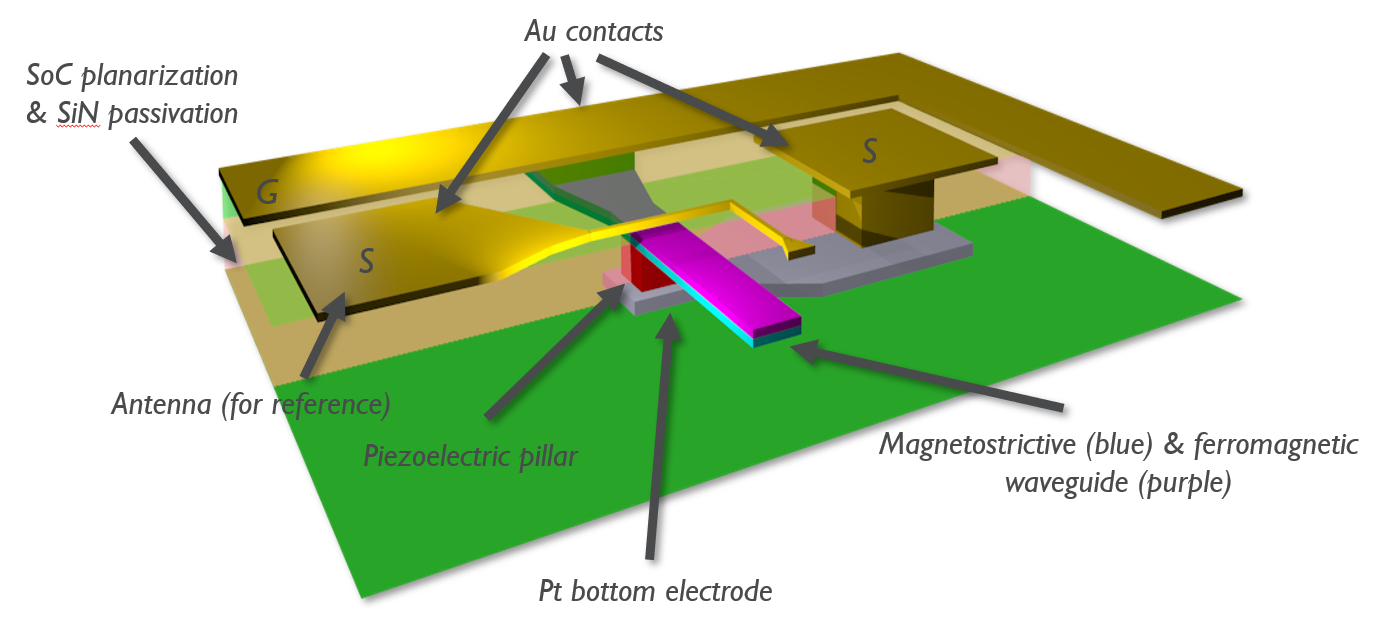
Of particular interest was the geometry of the transducer and the impact of the non-active surrounding layers on the effective magnetoelastic and magnetoelectric coupling. The “active” part of the structure consisted of a pillar including the magnetoelectric bilayer and two metal electrodes. In the same way, the experimental device structure is based on a magnetoelectric pillar transducer. Functional ME spin wave transducers down to 500 nm CD and up to 10 GHz has already been demonstrated. |
|
 |
| Top |